LeetCode 周赛323场
6257. 删除每行中的最大值
给你一个 m x n 大小的矩阵 grid ,由若干正整数组成。
执行下述操作,直到 grid 变为空矩阵:
- 从每一行删除值最大的元素。如果存在多个这样的值,删除其中任何一个。
- 将删除元素中的最大值与答案相加。
注意 每执行一次操作,矩阵中列的数据就会减 1 。
返回执行上述操作后的答案。
示例 1:
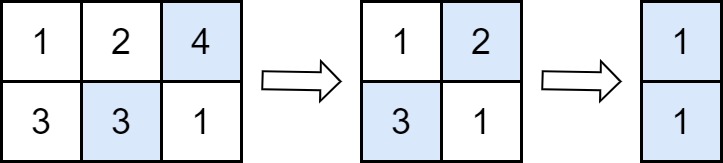
1 | 输入:grid = [[1,2,4],[3,3,1]] |
示例 2:
1 | 输入:grid = [[10]] |
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 501 <= grid[i][j] <= 100
解法:每次操作会让矩阵删除一列,最多删除n列,而后按照题意模拟即可
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution: |
6258. 数组中最长的方波
给你一个整数数组 nums 。如果 nums 的子序列满足下述条件,则认为该子序列是一个 方波 :
- 子序列的长度至少为
2,并且 - 将子序列从小到大排序 之后 ,除第一个元素外,每个元素都是前一个元素的 平方 。
返回 nums 中 最长方波 的长度,如果不存在 方波 则返回 -1 。
子序列 也是一个数组,可以由另一个数组删除一些或不删除元素且不改变剩余元素的顺序得到。
示例 1 :
1 | 输入:nums = [4,3,6,16,8,2] |
示例 2 :
1 | 输入:nums = [2,3,5,6,7] |
提示:
2 <= nums.length <= 1052 <= nums[i] <= 105
解法:由于是子序列,而且可以后续排序,所以我们可以拿到任意位置的数字,因此可以直接排序,当当前数确定时,前一个数就一定是这个数的开平方,所以有如下关系:
由于最多有 $10 ^ 5$ 个数,因此可以使用 $f[i]$ 来表示以i结尾的满足题意的个数
1 | class Solution { |
1 | class Solution { |
6259. 设计内存分配器
给你一个整数 n ,表示下标从 0 开始的内存数组的大小。所有内存单元开始都是空闲的。
请你设计一个具备以下功能的内存分配器:
- 分配 一块大小为
size的连续空闲内存单元并赋 idmID。 - 释放 给定 id
mID对应的所有内存单元。
注意:
- 多个块可以被分配到同一个
mID。 - 你必须释放
mID对应的所有内存单元,即便这些内存单元被分配在不同的块中。
实现 Allocator 类:
Allocator(int n)使用一个大小为n的内存数组初始化Allocator对象。int allocate(int size, int mID)找出大小为size个连续空闲内存单元且位于 最左侧 的块,分配并赋 idmID。返回块的第一个下标。如果不存在这样的块,返回-1。int free(int mID)释放 idmID对应的所有内存单元。返回释放的内存单元数目。
示例:
1 | 输入 |
提示:
1 <= n, size, mID <= 1000- 最多调用
allocate和free方法1000次
解法:由于数据量比较小,可以直接模拟,对于分配,可以记录最大连续的0的个数,如果等于size,那么对这段进行分配,否则返回-1,对于释放,直接模拟即可
1 | class Allocator { |
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 zaizwk!